Gene Patent Dispute: Pathology vs. Myriad
This is a case of Association for Molecular Pathology et al., Petitioners versus Myriad Genetics Inc. in USA
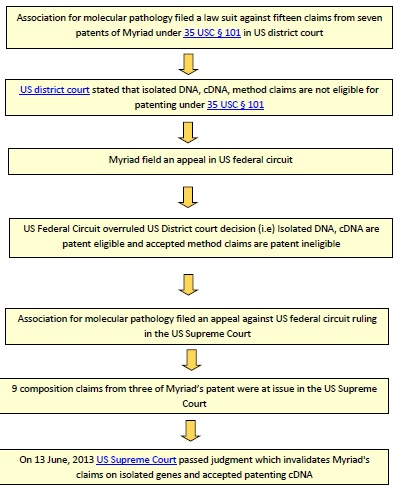
On June 13, 2013 United States Supreme Court declared that isolated human genes cannot be patentable because it is a product of nature and also said that cDNA can be patentable as it contains only exons and is not a naturally occurring one.
Myriad Genetics Inc. is a company which discovers and markets molecular diagnostic tools to predict patients in risk of developing diseases. Myriad Genetics have discovered precise location and sequence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene which are located on chromosome 17 and 13. These genes are commonly known as tumor suppressor genes which help to prevent unwanted cell growth. Mutation in these genes may cause hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Based on this discovery, Myriad introduced molecular diagnostic tool (BRACAnalysis®) for predicting hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. Myriad got several patents related to BRCA1 and BRAC 2 genes.
Petitioner Dr. Harry Ostrer along with medical patients, advocacy group and other doctors filed a lawsuit seeking declaration that fifteen claims from seven patents (US5747282, US5693473, US5837492, US5709999, US5710001, US5753441, US6033857) of Myriad’s covering BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene are invalid under U.S.C. $101 in the United States District Court Southern district of New York. Those fifteen claims had been divided into two types 1) Composition claim 2) Method claim
Composition claim
- Claim 01 of US5747282, US5837492 directed to an isolated DNA coding for a BRCA1 polypeptide and BRCA2 polypeptide
- Claim 02 of US5747282 directed to an isolated DNA of claim 01 and its sequence is listed in SEQ ID NO:1. SEQ ID NO:1 lists cDNA sequence of BRCA1 gene
- Claim 05 of US5747282 deals with an isolated DNA having atleast 15 nucleotides of claim 01
- Claim 06 of US5747282 deals with an isolated DNA having atleast 15 nucleotides of claim 02
- Claim 07 of US5747282, claim 06 and 07 of US5837492, claim 01 of US5693473 deal with an isolated DNA coding for a mutated form of BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Method claim
- Claim 01 0f US5709999, US5710001, US5753441, and claim 01 and 02 of US6033857 deals with a method for identifying / screening mutation in BRCA1 and BRCA2
On March 29, 2010 US district court declared that Myriad’s patents are invalid under 35 USC § 101. The court said that the composition claims deal with product of nature and method claims are like an algorithm which were not patentable under 35 USC § 101.
(35 U.S.C. 101 Inventions patentable – Whoever invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof, may obtain a patent therefor, subject to the conditions and requirements of this title)
Myriad filed an appeal against US District court’s decision in US federal circuit. Initially, US Federal Circuit overruled US District court decision stating that claims dealing with isolated DNA, cDNA are patent eligible and accepted the ineligibility of method claims to be patented. After the Federal Circuit ruling, the Association for Molecular Pathology filed a writ of certiorari to the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court granted the writ on March 26, 2012 and remanded the case back to the Federal Circuit. The second ruling of the federal circuit remains the same. On September 25, 2012 the American Civil Liberties Union and the Public Patent Foundation filed second writ of certiorari to the Supreme Court against Federal Circuit Decision and the Supreme Court agreed to hear the appeal on November 30, 2012.
The composition claims of US5747282 (claims 1, 2, 5, 6, and 7), US5693473 (claim 1) and US5837492 (claims 1, 6, and 7) were at issue. Finally on June 13, 2013 the US Supreme Court concluded that isolated human genes are not patentable under 35 USC § 101. But cDNA can be patentable as it is manipulated and does not exist in nature. cDNA (Complementary DNA) is artificially synthesized which contains only coding region of gene that does not available in nature.
On June 13, 2013 Myriad Genetics, Inc. Said that the Supreme Court of the United States upheld its patent claims on complementary DNA, or cDNA. Based on Supreme Court’s decision, Myriad has more than 500 valid and enforceable claims in 24 different patents conferring strong patent protection for its BRACAnalysis® test.
Myriad’s patient assistance program that provided free tests for more than 35,000 at-risk patients is laudable.
The case of Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics is important relating to human gene patenting.The Supreme Court’s decision of invalidating Myriad’s claims to isolated genes provide a clear understanding that merely isolated genes that are found in nature, discovering location and sequencing of gene do not have patent eligibility.
Below flow chart illustrates events relating to Myriad’s human gene patent case in USA, in a chronological order.












0 Comments